The female body is a complex and intricate system, characterized by unique physiological and anatomical features that distinguish it from the male body. One of the most significant aspects of female biology is the reproductive system, which includes structures such as the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and vagina. These organs are not only essential for reproduction but also play a crucial role in hormonal regulation.
Hormones like estrogen and progesterone are pivotal in governing various bodily functions, including menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and even mood regulation. Understanding these biological processes is fundamental for women to navigate their health effectively. Moreover, women experience distinct health challenges throughout their lives, influenced by factors such as age, genetics, and lifestyle choices.
For instance, during puberty, women undergo significant physical changes that prepare their bodies for potential motherhood. As they transition into adulthood, they may face issues related to menstrual health, fertility, and menopause. Each of these stages presents unique health considerations that require a tailored approach to wellness.
Additionally, women are more prone to certain conditions such as osteoporosis and autoimmune diseases, necessitating a deeper understanding of their bodies to promote long-term health and well-being.
Nutritional Needs for Women
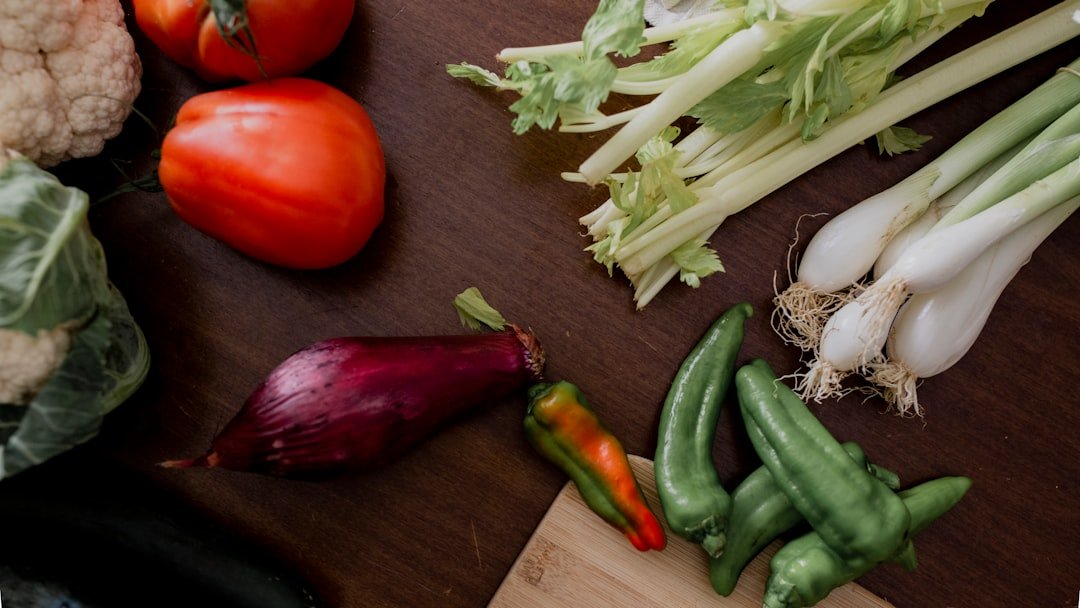
Nutrition plays a vital role in maintaining optimal health for women at every stage of life. The dietary requirements of women can vary significantly based on factors such as age, activity level, and reproductive status. For instance, during menstruation, women may require higher levels of iron due to blood loss.
Foods rich in iron, such as spinach, lentils, and red meat, can help replenish these levels. Additionally, calcium and vitamin D are crucial for bone health, particularly as women age and face an increased risk of osteoporosis. Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods are excellent sources of these nutrients.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women have even more specific nutritional needs. During pregnancy, the body requires additional calories and nutrients to support fetal development. Folate is particularly important during this time to prevent neural tube defects; sources include leafy greens, beans, and fortified cereals.
Postpartum nutrition is equally critical as it supports recovery and lactation. A balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of fruits and vegetables can help meet these increased demands while promoting overall health.
Superfoods for Female Health
Superfoods are nutrient-dense foods that offer exceptional health benefits and can be particularly advantageous for women. Berries, for example, are packed with antioxidants that combat oxidative stress and inflammation. Blueberries have been shown to improve cognitive function and may reduce the risk of heart disease.
Similarly, fatty fish like salmon are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential for heart health and may alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety—conditions that disproportionately affect women. Another superfood worth noting is quinoa, a complete protein that contains all nine essential amino acids. This makes it an excellent choice for vegetarians and vegans looking to meet their protein needs without animal products.
Quinoa is also high in fiber, which aids digestion and helps maintain a healthy weight. Incorporating superfoods into daily meals can enhance overall nutrition and provide specific benefits tailored to women’s health needs.
Hormonal Balance and Diet
Hormonal balance is crucial for women’s health and can be significantly influenced by diet. Fluctuations in hormones can lead to various symptoms such as mood swings, fatigue, and weight gain. Consuming a diet rich in whole foods can help stabilize hormone levels.
For instance, foods high in fiber can aid in the elimination of excess estrogen from the body, which is particularly important for preventing estrogen dominance—a condition linked to various health issues including fibroids and certain cancers. Healthy fats also play a vital role in hormone production. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts support the production of hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
Additionally, incorporating cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli and cauliflower can help metabolize estrogen effectively due to their high content of indole-3-carbinol. By focusing on a balanced diet that includes these elements, women can promote hormonal harmony and mitigate the symptoms associated with hormonal imbalances.
Meal Planning and Preparation
Effective meal planning is essential for maintaining a healthy diet tailored to women’s nutritional needs. By taking the time to plan meals ahead of time, women can ensure they are consuming a balanced diet that meets their specific requirements. This involves not only selecting nutrient-dense foods but also considering portion sizes and meal timing.
For instance, incorporating a variety of colors on the plate can help ensure a wide range of vitamins and minerals are consumed. Preparation methods also play a significant role in preserving the nutritional value of food. Steaming vegetables rather than boiling them can help retain water-soluble vitamins like vitamin Batch cooking grains or legumes can save time during busy weeks while ensuring that healthy options are readily available.
Additionally, keeping healthy snacks on hand—such as nuts or yogurt—can prevent unhealthy choices when hunger strikes unexpectedly.
Exercise and Its Role in Female Health
Exercise is an integral component of overall health for women, offering numerous physical and mental benefits. Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight, reduces the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes, and improves bone density—an essential consideration for women as they age. Weight-bearing exercises like walking or resistance training are particularly beneficial for building strong bones.
Beyond physical health benefits, exercise also plays a crucial role in mental well-being. Engaging in regular physical activity has been shown to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression while enhancing mood through the release of endorphins. Activities such as yoga or Pilates not only improve flexibility and strength but also promote mindfulness and stress reduction—factors that are especially important for women juggling multiple responsibilities.
Mindful Eating and Emotional Health
Mindful eating is an approach that encourages individuals to pay attention to their food choices and eating habits without judgment. This practice can be particularly beneficial for women who may experience emotional eating or disordered eating patterns due to societal pressures or stressors. By cultivating awareness around food intake—such as recognizing hunger cues or savoring each bite—women can develop a healthier relationship with food.
Emotional health is closely tied to nutrition; certain foods can influence mood and energy levels. For example, complex carbohydrates found in whole grains can boost serotonin levels in the brain, promoting feelings of well-being. Conversely, excessive consumption of processed foods high in sugar may lead to energy crashes and mood swings.
By practicing mindful eating techniques alongside a balanced diet, women can enhance their emotional resilience while fostering a positive relationship with food.
Seeking Professional Guidance for Optimal Health
Navigating the complexities of female health can be challenging; therefore, seeking professional guidance is often beneficial for achieving optimal wellness. Registered dietitians or nutritionists can provide personalized dietary advice based on individual health needs and goals. They can help identify nutrient deficiencies or dietary patterns that may be impacting overall health.
Additionally, healthcare providers specializing in women’s health can offer insights into hormonal balance, reproductive health, and preventive care strategies tailored specifically for women. Regular check-ups with gynecologists or endocrinologists can ensure that any potential issues are addressed early on. By collaborating with healthcare professionals, women can create comprehensive wellness plans that encompass nutrition, exercise, mental health support, and preventive care—ultimately leading to improved quality of life and longevity.
FAQs
What is a healthy diet for females?
A healthy diet for females includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. It is important to limit processed foods, added sugars, and unhealthy fats.
How many servings of fruits and vegetables should females have each day?
Females should aim to have at least 5 servings of fruits and vegetables each day. This can include fresh, frozen, or canned options.
What are some examples of lean proteins for females?
Lean proteins for females include chicken, turkey, fish, tofu, beans, lentils, and low-fat dairy products. These options provide essential nutrients without excess saturated fat.
What are healthy fats for females to include in their diet?
Healthy fats for females include avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These fats can help support heart health and provide essential nutrients.
How can females limit added sugars in their diet?
Females can limit added sugars in their diet by choosing whole fruits over fruit juices, opting for plain yogurt instead of flavored varieties, and reading food labels to identify hidden sources of added sugars.
Why is it important for females to stay hydrated as part of a healthy diet?
Staying hydrated is important for females to support overall health, digestion, and energy levels. It is recommended for females to drink at least 8-10 cups of water per day.